Reduction gearboxes
The gearboxes are manufactured with the following main components:
•Cast steel gearbox housing
•Input shaft arranged for flexible coupling
•Hydraulic operated multi- plate clutch for secure and soft engagement
•Gearwheels with hardened and ground helical teeth for silent operating
•Hydraulic built-in servo unit for secure propeller pitch setting
•Output shaft with flange arrangement for propeller shaft coupling
•All bearings of roller type with low friction losses and long lifetime
•Spherical roller thrust bearing with low friction losses and long lifetime
•All parts are made of the most suitable material qualities
Single stage reduction gearboxes with horizontal or vertical offset
The reduction gearboxes are designed for engines between 150 kW to 8000 kW. Maximum input speed is from 3200 rpm to 1000 rpm for the largest gearboxes and the reduction ratio is from 2:1 up to 10:1. The largest reduction is done by an additional gear train and the gearboxes can be delivered with PTO’s for hydraulic pumps or shaft generator.
GXU gearboxes
GXU gearboxes are designed for vessels where the size of the engine room is limited. The gearbox can be delivered with different center distances for the best possible arrangement in the engine room. The gearbox is engineered with a solid design for high reliability in operation. PTO’s for hydraulic pumps or shaft generator can also be delivered.
The GXU gearbox can be powered by diesel engines, liquefied natural gas (LNG) engines or e-motors. Typical vessels using this gearbox are: bulk carriers, general cargo vessels and live fish carriers.
Twin input – single output gearboxes
Twin input – single output gearboxes are often used when variable power to the propeller is required. The gearbox can be operated with one or two engines at the same time. In vessel were extra reliability is required this is a good solution. The engines can either be placed in front of or behind the gearbox. PTO’s for hydraulic pumps or shaft generator can also be delivered.
The twin input- single output gearbox gives a flexible solution. By using the correct combination of main engines and e-motors, the fuel consumption and emissions are reduced. The system gives flexibility, redundancy and safety. The gearboxes can be powered by diesel engines, liquefied natural gas (LNG) engines, e-motors or a combination of this.

2- speed gearbox
The 2- speed gearbox are used on vessels with large difference in power need. This configuration has the following advantages:
•Two different propeller speeds at a constant engine speed
•The propeller can be operated at optimal speed both at high and low load
•Minimized zero pitch loss at “low gear”
•Minimized propeller noise at “low gear”
•Fuel saving at low load
In high gear, clutch 1 is engaged and clutch 2 is disengaged, meaning full engine power can be given to the propeller, and excess power to the shaft generator. In low gear, clutch 1 is disengaged and clutch 2 is engaged, resulting in reduced engine power to the propeller due to lower propeller speed, and excess power to the shaft generator. Both gears allow for uninterrupted work of the generator at a constant speed of Power Take- off shaft. Additionally, the gearbox can be constructed with a 3rd clutch for disengaging the shaft generator when needed.
In addition to the two- speed gearbox, the vessel can also utilize floating frequency, allowing the engine speed to be lowered in “generator mode”. Variations in the engine speed which correspond to the floating frequency of the shaft generator from 50 Hz to 60 Hz allows for optimal propeller speed in the full operating range.
Hybrid propulsion
A hybrid propulsion system is suitable for ships with variable power requirements, enabling the engines and propellers to run optimally over a wide power range. The e-motor can be with a synchronous speed, but in order to have optimal propeller speed it is preferable to control the speed with a frequency converter for fuel savings and lower emissions.
The hybrid propulsion system combines the best from two systems; diesel, electric and diesel mechanical propulsion. Diesel mechanical drive is used for transit from A to B. For standby, DP or other operations modes with a benefit of variable propeller speeds diesel electrical drive is applied.
"Boost" drive means that the main engine and electric motor is operating together, for maximum power, which most often is used for heavy loads like towing, anchor handling or trawling. Applying an electrical motor in case of main engine breakdown is known as a “Take me home" drive. Ranging from basic to more complex configurations, a large number of operational modes are available.

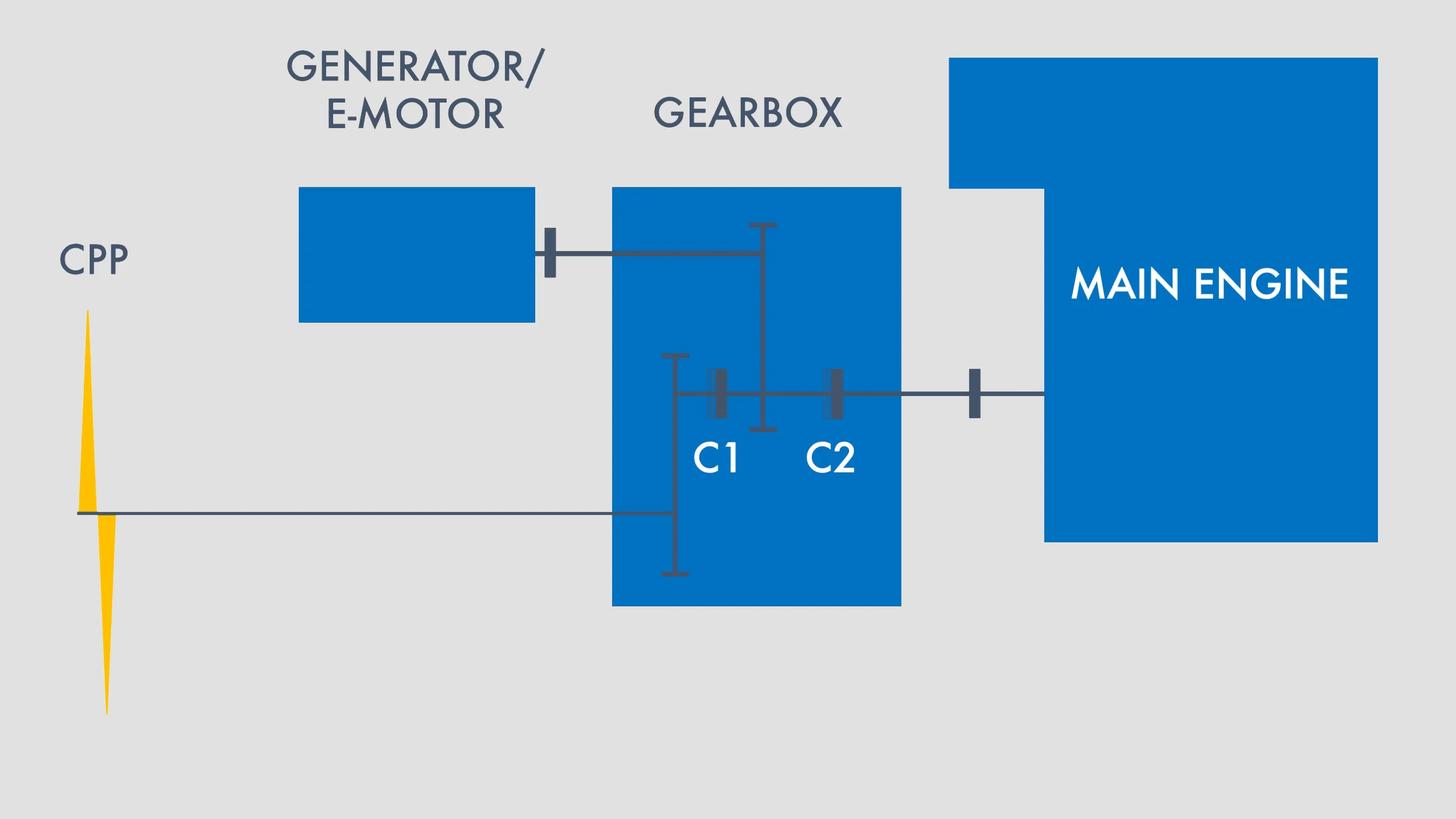
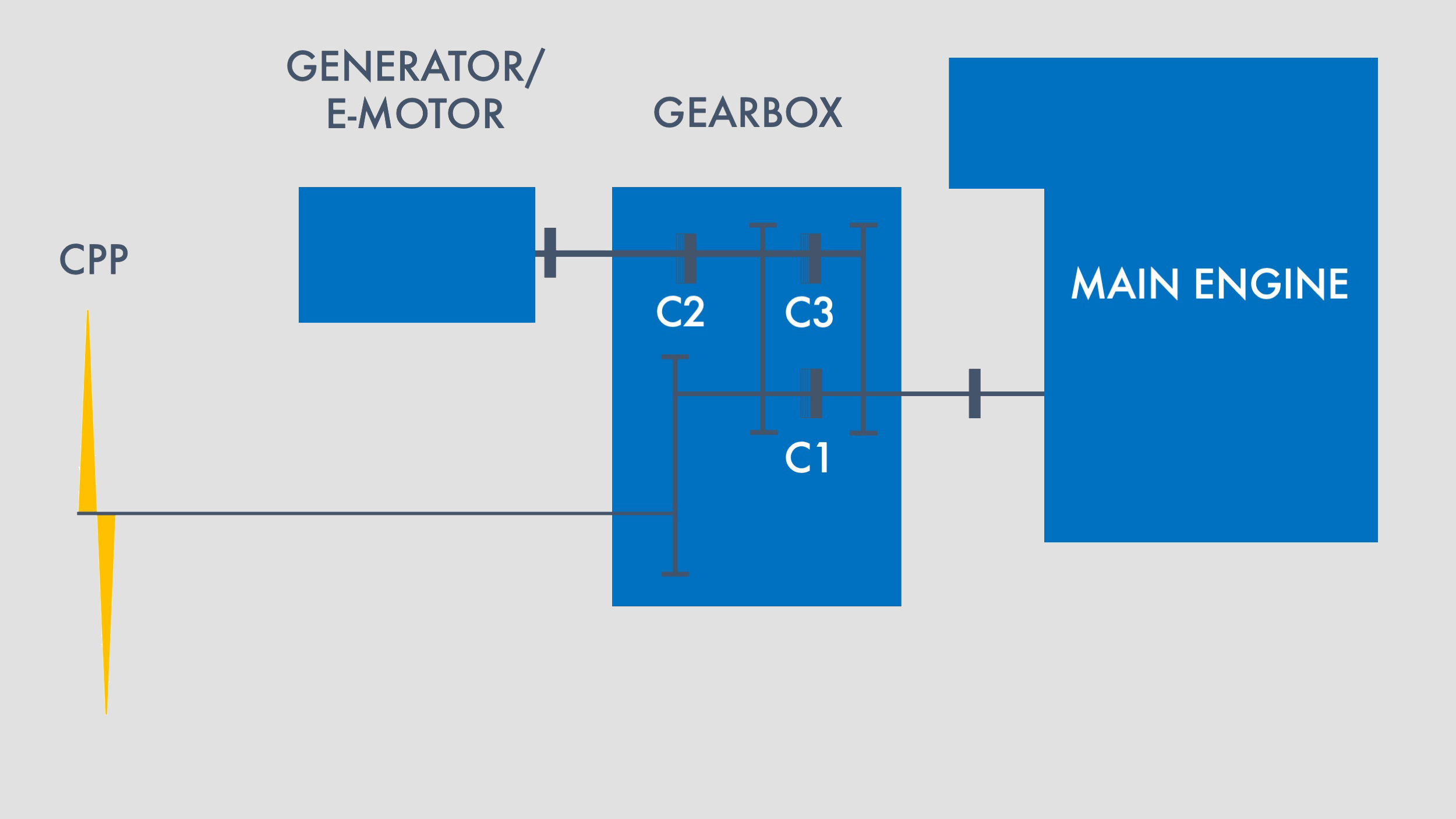
Twin input – single output gearboxes
PTO/PTI connected prior to the main clutch (C1 – C2). With separate clutches (C3) and (C4) on the main engine. This feature is also used on twin screwed vessels, giving the possibility to operate the vessel with only one main engine running.
Electric propulsion
This configuration is mainly used for ships with large capacity of electric power in combination with large differences in propulsion power. This configuration has the following advantages:
•Optimum propeller speed over the whole operating range
•Minimized zero pitch loss
•Fuel saving at low load


